ITSec EU Limited presently provide ISO 27001 Certification Service for government departments, NGO, global banks, financial service providers, multi-national companies and merchants… The ISO27001 is a globally recognized international standard for Information Security management system (ISMS).
In the digital age, information security has become a critical concern for businesses of all sizes. From small businesses to large enterprises, everyone is striving to protect their data and maintain the trust of their clients. One way to achieve this is through ISO 27001 certification.
What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001 is the internationally recognized standard for information security management systems. It was adopted by the International Standards Organization (ISO) in 2005 and updated in 2013. Certification demonstrates that an organization has designed and implemented a comprehensive information security management system that meets the highest standards.
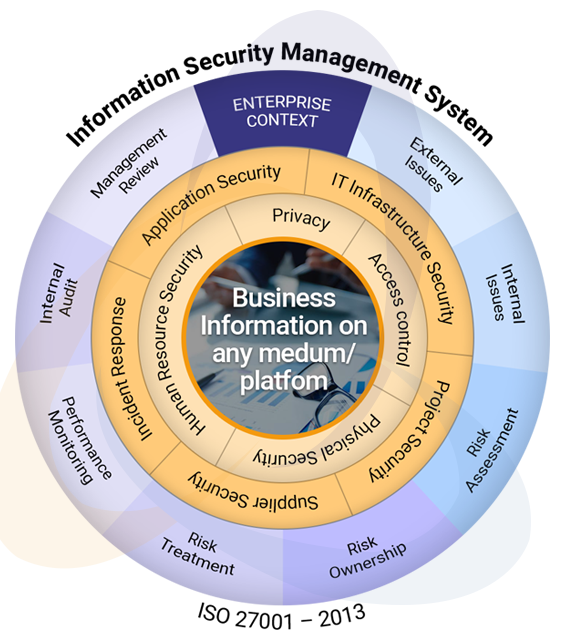
The ISO 27001 Guidelines provide a framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS). These guidelines are globally recognized and followed by businesses in various regions. The ISO 27001 Requirements are designed to help organizations manage their security practices in line with international best practices.Achieving ISO 27001 Certification involves a rigorous process. It begins with understanding the ISO 27001 Certification Process, which includes a series of audits and reviews to ensure compliance with the standard. Businesses must also adhere to the ISO 27001 Best Practices, which provide guidance on implementing effective security controls.
Benefits of ISO 27001 Certification
There are numerous benefits to achieving ISO 27001 Certification. For one, it demonstrates to clients and stakeholders that your business takes information security seriously. Many ISO 27001 Certified Companies have reported increased trust from their clients and improved business relationships. Moreover, the certification helps businesses improve their data security standards. By following the ISO 27001 Risk Management guidelines, businesses can identify potential security risks and implement measures to mitigate them. This proactive approach to risk management can prevent data breaches and protect sensitive information.
- Reduce risk: reduce the possible risk of fraud, information loss and disclosure
- Demonstrate integrity: demonstrate the integrity of your data and systems to existing and potential customers, suppliers and shareholders
- Gain new business: create new business opportunities with security conscious prospects by standing out from the competition
- Meet GDPR requirements: security management certifications are key to complying with GDPR standards
Exploring ISO 27001 Certification Requirements and Compliance
The requirements for ISO 27001 Certification include the development of a security policy, the definition of risk assessment approaches, the identification of risks, and the implementation of security controls. Compliance with these requirements demonstrates that your business takes data protection seriously. It also ensures that you have a clear understanding of what needs to be done to protect your information assets.
The Role of ISO 27001 Certification Audit in Implementation
The ISO 27001 audit is a crucial part of the certification process. It involves a thorough examination of your ISMS to ensure it meets the standard’s requirements. The implementation guide can be a valuable resource during this process. It provides step-by-step instructions on how to implement an ISMS and prepare for the audit.
Typical certification process
- Initial consultation: to understand your organization and priorities so we can build a custom proposal
- Training (optional): in-person or online to get your organization up to speed quickly
- Pre-assessment (optional): to ascertain your readiness for certification
- Desk study: remote appraisal of your documentation to prepare for an on-site assessment
- On-site certification audit: our experienced auditors will visit your facility to complete the final assessment
Key Steps in ISO27001 Certification
Gap Analysis:
- Understanding of your organization and its context,
- define certification scope of ISMS,
- identify information security risks and risk owners,
- assess existing information security practices viz-a-viz 27001 requirements.
Initial Review and Planning:
- Review the findings of gap analysis by Senior Management,
- conduct corresponding information security risks treatment,
- establish a cross-functional information security team headed by a senior manager,
- plan for 27001 implementations.
Documentation:
Preparation of manuals, forms, etc.
Implementation:
Implementation of the system as per manuals.
Company-wide Training:
Training on 27001 requirements, ISMS documentation, good ISMS practices, internal ISMS audit, etc.
Internal Audit:
conduct periodic internal audit(s) of ISMS implementation.
Initial assessment:
Initial assessment by the chosen Certification Body & corrective actions on identified issue(s).
Final Assessment:
Detailed assessment by the Certification Body and recommendation for certification.
Achieving ISO 27001 Compliance
Achieving ISO 27001 Compliance involves meeting all the requirements of the standard. This includes implementing effective security controls as outlined in the ISO 27001 Security Controls list. Businesses must also ensure that they uphold confidentiality and ethics in all their operations.
The journey towards compliance also involves regular audits. The ISO 27001 Audit Checklist provides a comprehensive list of areas that auditors will review during an audit. By preparing for these audits, businesses can identify areas of non-compliance and take corrective action.

ISO 27001 Certification can play a vital role in strengthening your business’s information security posture. Whether you’re an IT company or any other type of business, achieving this certification can provide significant benefits. Remember, information security is not just about implementing software solutions; it’s about establishing robust processes to manage risks effectively.
By incorporating these keywords into your website content and optimizing them for SEO, you can improve your visibility on search engines like Google and Bing. However, remember that SEO is not just about using keywords; it’s also about providing valuable and relevant content to your audience.
Our ISO27001 Certification Consultation Services
We provide consultancy service to facilitate & support our client’s ISO27001 certification. With overyear ISO27001 implementation experience, we have effective and efficient mechanism to save our clients’ time and money. Typical Scope of Work (SOW) involves the followings:
(1) Gap Analysis
- Identify gaps between existing client’s ISMS implementation against ISO 27001:2013 standards.
- Provide Gap Closure advises & support to client for remediations.
- Deliverable:
- ISMS Gap Analysis Report against ISO 27001:2013 standard
(2) Ready-To-Use Documentation & Process for Compliance
- Assist client to define proper ISO 27001:2013 scope statement
- Assist client to define the certification Statement of Applicability (SOA)
- Provide Proven & Ready-To-Use Policy, Standard, and Procedure documentation templates to client, and assist client‘s adoption.
- Deliverable:
- ISO 27001:2013 scope statement and Statement of Applicability (SOA) sample – source from successfully ISO27001 certified body
- Ready-To-Use ISO 27001:2013 documentation template – source from our previous successful ISO27001 certification
(3) Training on ISO27001:2013 Certification & Maintenance
- Provide training to client’s Information Security Team for ISO 27001:2013 certification & on-going maintenance
- Deliverable:
- Training Program on ISO27001:2013 Framework, Control Measures Introduction & Compliance Requirements
(4) Internal Audit (Pre-Assessment walk-thru)
- Perform Internal Audit (as well as pre-assessment walk-thru) before official certification audit
- Deliverable:
- Internal Audit Pre-Assessment Audit Report benchmark against ISO 27001:2013 standard; identify any non-conformity for client remediation before official certification audit
(5) Onsite Support during official certification audit
- Attend the official certification audit (to be conducted by client’s selected Certification Body) & act as member of client’s ISO27001:2013 certification team in facilitating the successful ISO27001:2013 certification

ISO27001 Content
ISO 27001:2013 is divided into ten clauses, an Annex and a Bibliography
ISO 27001:2013 Ten (10) clauses are:
- Scope
- Normative References
- Terms and Definitions
- Context of the Organization
- Leadership
- Planning
- Support
- Operation
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement
ISO 27001:2013 Annex A
ISO 27001:2013 Annex A is a vital part of the ISO 27001 standard, with Annex A5-A18 states all the reference controls of the ISO 27001 standard.
A5 Information security policies
- A5.1 Management direction for information security
- 5.1.1 Policies for information security
- 5.1.2 Review of the policies for information security
A6 Organizing information security
- A6.1 Internal organization
- 6.1.1 Information security roles and responsibilities
- 6.1.2 Segregation of duties
- 6.1.3 Contact with authorities
- 6.1.4 Contact with special interest groups
- 6.1.5 Information security in project management
- A6.2 Mobile devices and teleworking
- 6.2.1 Mobile device policy
- 6.2.2 Teleworking
A7 Human resource security
- A7.1 Prior to employment
- 7.1.1 Screening
- 7.1.2 Terms and conditions of employment
- A7.2 During employment
- 7.2.1 Management responsibilities
- 7.2.2 Information security awareness, education, and training
- 7.2.3 Disciplinary process
- A7.3 Termination and change of employment
- 7.3.1 Termination or change of employment responsibilities
A8 Asset management
- A8.1 Responsibility for assets
- 8.1.1 Inventory of assets
- 8.1.2 Ownership of assets
- 8.1.3 Acceptable use of assets
- 8.1.4 Return of assets
- A8.2 Information classification
- 8.2.1 Classification of information
- 8.2.2 Labelling of information
- 8.2.3 Handling of assets
- A8.3 Media handling
- 8.3.1 Management of removable media
- 8.3.2 Disposal of media
- 8.3.3 Physical media transfer
A9 Access control
- A9.1 Business requirements of access control
- 9.1.1 Access control policy
- 9.1.2 Policy on the use of network services
- A9.2 User access management
- 9.2.1 User registration and de-registration
- 9.2.2 User access provisioning
- 9.2.3 Privilege management
- 9.2.4 Management of secret authentication information of users
- 9.2.5 Review of user access rights
- 9.2.6 Removal or adjustment of access rights
- A9.3 User responsibilities
- 9.3.1 Use of secret authentication information
- A9.4 System and application access control
- 9.4.1 Information access restriction
- 9.4.2 Secure log-on procedures
- 9.4.3 Password management system
- 9.4.4 Use of privileged utility programs
- 9.4.5 Access control to program source code
A10 Cryptography
- A10.1 Cryptographic controls
- 10.1.1 Policy on the use of cryptographic controls
- 10.1.2 Key management
A11 Physical and environmental security
- A11.1 Secure areas
- 11.1.1 Physical security perimeter
- 11.1.2 Physical entry controls
- 11.1.3 Securing offices, rooms and facilities
- 11.1.4 Protecting against external and environmental threats
- 11.1.5 Working in secure areas
- 11.1.6 Delivery and loading areas
- A11.2 Equipment
- 11.2.1 Equipment siting and protection
- 11.2.2 Supporting utilities
- 11.2.3 Cabling security
- 11.2.4 Equipment maintenance
- 11.2.5 Removal of assets
- 11.2.6 Security of equipment and assets off-premises
- 11.2.7 Secure disposal or re-use of equipment
- 11.2.8 Unattended user equipment
- 11.2.9 Clear desk and clear screen policy
A12 Operations security
- A12.1 Operational procedures and responsibilities
- 12.1.1 Documented operating procedures
- 12.1.2 Change management
- 12.1.3 Capacity management
- 12.1.4 Separation of development, test and operational environments
- A12.2 Protection from malware
- 12.2.1 Controls against malware
- A12.3 Backup
- 12.3.1 Information backup
- A12.4 Logging and monitoring
- 12.4.1 Event logging
- 12.4.2 Protection of log information
- 12.4.3 Administrator and operator logs
- 12.4.4 Clock synchronization
- A12.5 Control of operational software
- 12.5.1 Installation of software on operational systems
- A12.6 Technical vulnerability management
- 12.6.1 Management of technical vulnerabilities
- 12.6.2 Restrictions on software installation
- A12.7 Information systems audit considerations
- 12.7.1 Information systems audit controls
A13 Communications security
- A13.1 Network security management
- 13.1.1 Network controls
- 13.1.2 Security of network services
- 13.1.3 Segregation in networks
- A13.2 Information transfer
- 13.2.1 Information transfer policies and procedures
- 13.2.2 Agreements on information transfer
- 13.2.3 Electronic messaging
- 13.2.4 Confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements
A14 System acquisition, development and maintenance
- A14.1 Security requirements of information systems
- 14.1.1 Security requirements analysis and specification
- 14.1.2 Securing application services on public networks
- 14.1.3 Protecting application services transactions
- A14.2 Security in development and support processes
- 14.2.1 Secure development policy
- 14.2.2 Change control procedures
- 14.2.3 Technical review of applications after operating platform changes
- 14.2.4 Restrictions on changes to software packages
- 14.2.5 System development procedures
- 14.2.6 Secure development environment
- 14.2.7 Outsourced development
- 14.2.8 System security testing
- 14.2.9 System acceptance testing
- A14.3 Test data
- 14.3.1 Protection of test data
A15 Supplier relationships
- A15.1 Information security in supplier relationships
- 15.1.1 Information security policy for supplier relationships
- 15.1.2 Addressing security within supplier agreements
- 15.1.3 Information and communication technology supply chain
- A15.2 Supplier service delivery management
- 15.2.1 Monitoring and review of supplier services
- 15.2.2 Managing changes to supplier services
A16 Information security incident management
- A16.1 Management of information security incidents and improvements
- 16.1.1 Responsibilities and procedures
- 16.1.2 Reporting information security events
- 16.1.3 Reporting information security weaknesses
- 16.1.4 Assessment of and decision on information security events
- 16.1.5 Response to information security incidents
- 16.1.6 Learning from information security incidents
- 16.1.7 Collection of evidence
A17 Information security aspects of business continuity management
- A17.1 Information security continuity
- 17.1.1 Planning information security continuity
- 17.1.2 Implementing information security continuity
- 17.1.3 Verify, review, and evaluate information security continuity
- A17.2 Redundancies
- 17.2.1 Availability of information processing facilities
A18 Compliance
- A18.1 Compliance with legal and contractual requirements
- 18.1.1 Identification of applicable legislation and contractual requirements
- 18.1.2 Intellectual property rights (IPR)
- 18.1.3 Protection of records
- 18.1.4 Privacy and protection of personal information
- 18.1.5 Regulation of cryptographic controls
- A18.2 Information security reviews
- 18.2.1 Independent review of information security
- 18.2.2 Compliance with security policies and standards
- 18.2.3 Technical compliance inspection
ISO 27001 Related Documents:
https://www.isaca.de/sites/default/files/isaca_2017_implementation_guideline_isoiec27001_screen.pdf







Find Us immediately for the Security Assessment in Hong Kong, United Kingdom, Europe, Estonia, Singapore…
Case Reference: